As an entrepreneur, you may be wondering why tech companies are valued so high. It all boils down to the fact that people outside of the industry don’t know how much work to do to make a successful company.
You have to keep up with technology trends and make sure your product is constantly updated to stay competitive in the market.
The more money a company has, the better it can invest in research and development for new products. But even then, there’s no guarantee that they will succeed.
In reality, many startups fail because their business model isn’t sustainable or because they couldn’t get enough funding from investors or loans from banks.
Tech companies are valued high because they seem to be positioned in an industry with an excellent trajectory. When you look at the market size of the tech industry, it is quite large and seems to expand rapidly based on new technologies that are constantly being released.
An excellent example of this is when iPhones came out. The sales for iPhones exploded when they were introduced (completely taking over profits in retail) because they matched so well with human needs of having access to music/videos/pictures etc., anytime, anywhere without searching for a computer or TV screen.
Tech companies are also valued so high because they have a huge fan base that grows endlessly through word-of-mouth marketing.
One might think that the number of users is not necessary to tech companies, but some startups like ZocDoc and Dropbox started with no more than one user.
Take ZocDoc, for example! The company’s success story is very straightforward. Founder Nicki Sheller could not find a doctor in New York City for her foot pain, so she created her practice through connections on Facebook. That, ladies and gentlemen, is one patient who happily became an evangelist of the service before it had even opened its doors!
When a tech company has more users, it will use its size and reach to build products faster and better than smaller companies.
The more usage a product or service has, the more likely it is for companies to build advertising strategies around that product or service. As today’s consumers are looking for new and unique brands they can identify with, many businesses are turning their focus towards obtaining mass-market attention online.
Tech startups show profitability through growth and retention rates, among other factors such as usability and engagement.
Tech startups take several years before there’s any profit to share with investors. During that time, investors support them with money and resources to help reach milestones that bring an eventual return on investment.
The tech company ecosystem is like a casino for venture capitalists, which means the risks are high, but so are the rewards. The tech industry offers the opportunity to make vast amounts of money in a concise amount of time and has enormous potential to falter.
Consider Microsoft when it went public in 1986 with an IPO at $21 per share – it’s currently valued at almost double that ($43).
Apple’s net profit for the 4th quarter of 2015 was $18 billion, or about 9% of its total revenue.
The more people who use Facebook, Gmail, or Youtube, the more page views and advertisements they produce – so even though they aren’t making money on their products per se, they are indirectly generating revenues through ad sales.
It is not only about the money; it’s about what you’re doing with your company daily. The more value you have, the higher your company will be worth at its current market price.
Ultimately it’s hard to say precisely why tech companies are valued so high by Silicon Valley culture. If you think that valuation means “profit potential,” then clearly, these companies have plenty of untapped markets with untapped profits waiting to be made.
Why Are Tech Companies Not Profitable?
Tech companies have been around for a while now, but most are still not profitable. It seems that tech businesses invest more money than they bring in, and there is a lot of speculation about why this is the case. There are many possible reasons, some of which we will discuss below.
First off, it could be due to their business model; tech companies might be spending more on marketing and advertising than what they make from their products or services.
Or maybe it’s because of an influx in competitors; as competition grows with each passing day, new startups crop up every few months, and old ones fall by the wayside even quicker than before, making it difficult for older firms to maintain profitability.
The tech industry has been known to have a higher frequency of financial volatility due to its accelerated investing cycles and growth patterns.
Most tech companies fail because they do not profit, meaning they cannot cover the cost of capital investments needed for future growth.
This is how financially stable tech firms can price themselves out of sustainable competition with lower-quality firms willing to take on debt or sacrifice best practices to compete with better-quality products.
There are many reasons why technology companies lose money, but three primary reasons are the following:
- It is trying to change itself too quickly. Apple is a great example of this – the company’s often thinking about ceasing phone manufacturing and just becoming an app developer. What they need to do in order to be profitable again is stay in their lane and produce quality products that people want to buy with regularity.
- Tech companies are betting too much on virtual reality and augmented reality when no one really knows if it’ll catch on or not, plus its expensive technology.
- They’re focusing too much on novelty rather than reliability when it comes to product designs. When you can’t rely on something, it creates difficulties for the company, such as investing in the production of overpriced commodity hardware over time.
It’s simply brutal these days to start a successful business, especially if it’s technologically oriented or heavily reliant on data science for its business prowess or funding strategies.
The causes of the lack of profitability are varied and complex. For one, many companies have a high cost-to-sales ratio which is not sustainable for long periods. Companies should note that they need to be profitable to keep investors happy and maintain growth over time.
Many factors go into whether or not a technology company will achieve profitability. Still, it’s essential to look at each one individually before making assumptions about your digital marketing strategy.
Why Are Tech Stocks So Overvalued?
If you’re looking for a quick answer to this question, I’m sorry to disappoint you, and there isn’t one. There are many reasons why tech stock prices may be inflated, and you must understand them before investing your hard-earned money.
It can be hard to keep up with the ever-changing world of technology. With innovations coming out every day, it’s easy to get lost in all the noise and not know what is worth paying attention to. But there are some trends that you should start paying attention to.
Tech stocks are valued high because their IPOs (initial public offering) tell the story of company growth in revenues and profits. Investors want in on the action, where all the buzz comes from about tech stock buybacks. Those buybacks are sparking more interest in a company’s future potential for profit growth, which adds to investor excitement and bids up prices on those shares of stock even higher. When a snowball starts rolling down a hill, it gathers more snow as it goes, producing an avalanche effect.
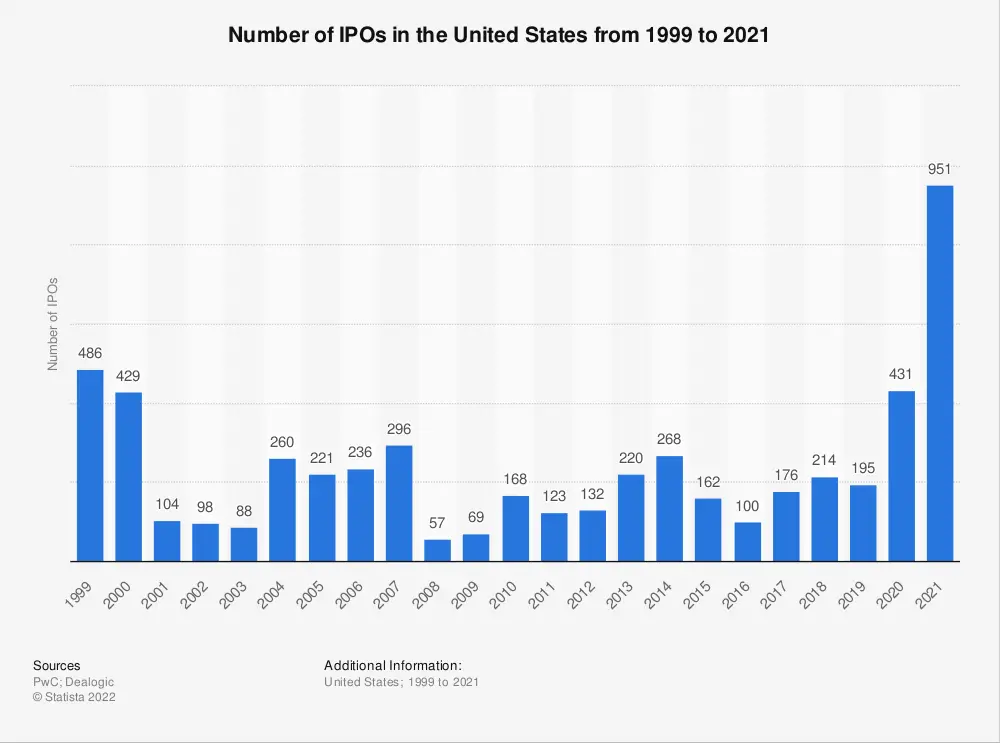
The market is fueled by fear and greed, and many investors lack a realistic understanding of what’s actually behind any given company. It leads to irrational speculation and an incredible rise in the valuation of companies that don’t have rock-solid fundamentals.
Any fundamental growth drivers do not support the massive valuations of many tech companies.
Many of the most successful giants in the industry have failed to turn a profit year-to-date, with significant losses recorded by Twitter, Fitbit, GoPro, Squarespace, and Pandora.
Valuations are being driven primarily by IPOs rather than organic business growth.
This decade’s tech boom was not driven by the innovations themselves but rather through the burgeoning population’s hunger for faster connectivity and faster computers, which allowed them limitless access to information – “connectivity is king.”
In conclusion, it is difficult to determine the actual value of a company’s worth when its market capitalization changes today. Investors should be wary in dealing with these stock prices because some stocks may not be as good as they seem on paper.
How Do You Value A High Growth Company?
Many factors go into deciding what constitutes “high growth.” Some people use revenue; others use earnings per share or net income. And then, there is the rate of return on equity (ROE) is often used to measure how well management can allocate capital and generate shareholder returns.
First, review the company’s growth rates, profitability, market share. Then compare these metrics with comparable companies in the industry. Once you’ve taken a look at all the essential information and figures from their last reporting period or year, understand how much product is being sold overall while also looking to see what percentage of total products under consideration are its own.
The key to valuing any business is understanding its future potential and how that will translate into earnings. Growth companies, such as those in the tech space, can be especially tricky to evaluate because they’re often still developing their products and services. However, there are some general steps you can take when assessing this type of company:
- What is the present value of all costs and revenues over the next 10 years?
- Regress data from similar companies on some key performance drivers with this company.
- Determine how large a terminal value should be, given the cost of equity and revenue volatility characteristics.
- What is your estimate for future cash flows?
- How cheaply could a competing startup duplicate your company’s business model?
- How “smart” are existing management teams/owners?
The valuation of a company is the opinion given by a company’s securities analysts on its future earnings.
Finance experts may also provide their estimates for which companies are overvalued and undervalued, but that doesn’t mean they can profit from those estimates.
Valuation depends not only on the prospects for success but also on the assumptions about the likelihood of future events.
If you are interested in investing, you should look for companies with a long-term sustainable growth strategy. Asking questions about how the company will achieve its goals and where it will get its funds from can help determine if this investment opportunity might fit your needs.
For example, look at Facebook’s IPO, which was delayed because of their need to raise additional capital. With so many high growth opportunities available, what do you think makes an investment worthwhile?
Valuation Multiples For High Growth Companies
The key to growing your business is the ability to understand the value of what you are creating. One way to measure this is by how much someone would be willing to pay for shares in your company or an equity valuation.
A company’s valuation is determined by the market and how much investors are willing to pay for a share of stock. More than just focusing on one metric, which can be misleading, it is essential that you look at all metrics to come up with an accurate value for the business. There are many different ways to measure this, but valuation multiples are among the most popular because they help show what other people think about your company.
What are valuation multiples? A company’s market value can also be calculated or expressed in its share price multiplied by the total number of shares outstanding.
There are two types of growth securities.
- The first one is a “slow grower” with relatively slow revenue and earnings growth rates but with low risk because it steadily pays off its debt at a regular pace without any default risk even though it may have less return on equity than other stocks in the same industry.
- The other type is a “high-growth” stock, which has high potential for appreciation if their increase in revenue and earnings exceed expectations.
The valuations of high-growth companies are based on the company’s ability to generate revenue and profit.
If a business is not achieving these goals, it won’t be easy to command such a high valuation.
Businesses mustn’t take shortcuts when it comes to making decisions about their future success, as this could lead to serious financial problems down the road. When you’re considering your next move in business, think long-term and make sure you’re taking all possible risks into account before committing any resources or time.
How Do You Evaluate Company Growth?
There are many ways to measure company growth, and you can look at your sales, profits, or even the number of new customers you have acquired. It is essential to measure these things to see how well your business is doing and what areas need improvement.
The most accurate method of determining company growth is to use revenue, which determines how well the business has been doing in recent years—also, examining the volume of product being produced. Comparing volume changes over time tells how much production is being done.
A company could make the same amount of sales each year without actually growing if its costs go up each year.
The best measure for growth would be to calculate the percentage change in revenue from one year to another.
Another helpful tool is calculating turnover rates, or annual sales per employee per dollar invested-this gives you an idea of whether existing employees are performing at a high level, squeezing high returns out of your investment, giving you room to hire more people if needed with low risk that new hires will not easily fit into an already thriving culture.
The need to evaluate company growth cannot be overstated. Considering change can help you better understand how big your company should be, whether you are growing properly based on your industry, or what strategies could work best to drive the right kind of success to fuel your business.
Your answers might vary depending on what goal you have in mind when evaluating company growth.
Here are three different ways to evaluate company growth.
- Market share increase – an increase in the percentage of total sales accounted for by a particular company. It can also be referred to as market penetration. Market share is calculated by taking the largest company’s market share less all other companies’ shares, which equals one.
- Profit or loss – this is not often reported but an important factor when evaluating growth potential for a business with no debt, high cash flow and low spending on fixed assets (such as R&D).
- Growth opportunities – growth will most likely only come from additional revenues generated from existing products/services or new ventures yet to make significant revenue contributions to the bottom line success of operation.
So, how do you evaluate company growth? It’s not as straightforward as it may seem. Your bottom line, revenue, is a great place to start and can be an indicator of your company’s success in the short term.
But what about long-term goals like team size or industry recognition? These are also essential factors that should play into any evaluation process for company growth.
Conclusion
A company’s valuation is the price at which an investor would be willing to pay for one share of that company.
Valuation multiples are a way of judging how much investors believe in future growth by comparing current market capitalization with some measure of sustainable profitability, such as earnings or cash flow.
The higher the ratio, the more expensive it is to buy into that stock because there is more significant uncertainty about what will happen if things go wrong.
Investors are typically looking forward 3-5 years when they evaluate whether or not a high-growth tech company’s valuations make sense based on their expected performance over time.
Quick Answers To Frequently Asked Questions
Do SaaS companies perform better recurring revenue?
Yes. One of the few advantages a Saas company has is that it can offer a lower-priced product to a more significant number of customers, which means their customer base will be considerably more important than the revenue from upfront payments from subscription clients.
Is there a market cap on a startup valuation?
It depends on the young company. A startup valuation is different in its infancy versus if it’s in potential “danger” of imploding. For example, a startup with no revenue would need to have an extensive track record of innovative solutions and wise leadership to be valued at over $500 million pre-money. On the other hand, a company that looks like they’re about to buckle under pressure might only be worth around $200 million for all their assets put together.
Is a unicorn company more desirable to a venture capitalist?
No, unicorn companies do not offer venture capitalists anything they cannot already get.
Difference between company valuation and private valuation?
A company valuation estimates the company’s probable worth based on past performance, future forecast, and comparables with similar companies. Usually, this value reaches far into the billions of dollars. At the same time, a private valuation is typically speculative with no established benchmark or guideline for comparison.
What does it mean to have a tech IPO on the public market?
In the simplest terms, it means you’re paying an early adopter fee to buy a share of a company even before they’ve been publicly available.
Does revenue multiple increase the growth rate for higher valuation?
It depends on the company. Generally, the more profitable a company is the higher its revenue multiple. But many companies have more excellent growth rates with smaller multiples because they reinvest their capital or possess valuable intangible assets that are not easy to measure.
What competitive advantage does a tech giant have?
When an organization competes in another’s market, the act of entry is often referred to as disruptive innovation. A key trait that defines a disruptive innovation is that it does not provide the incumbent company with business models or products that would cause it much harm.
Do venture investors want to see a business valuation first?
Yes, especially if the business valuation is well-done. This is to try and gauge the investment potential of the company they are looking at acquiring. The higher the quality of your appraisal, the better off you will be when signing an investor agreement. It always helps to be transparent with businesses that may want to invest in what you have created. This can help attract investors who can see how well your company’s worth reflects on their business opportunities.
Does an angel investor do post money valuation for the tech sector?
An angel investor is not generally involved in valuations using post-money because they invest in pre-money companies. When they decide how much to put into a company, the valuation is determined by the founders.
Does real estate receive venture capital funds?
Yes, real estate receives venture capital funds to a lesser degree than other sectors. However, many wealthy people were scammed by Bernie Madoff and other con-artists with their life savings tied up in the stock market.
What does it mean for large companies to have pre money valuation?
Large companies usually have this, and it means that the amount of money they contributed to themselves is more than the amount an outsider is willing to invest. This signals they are successful.
Difference between a private company and a public company?
A company that sells shares is a public company. Investors buy shares of the company’s stock, which represent ownership in the corporation. The price of each share reflects its value on the open market. A private company only has one owner rather than many shareholders, so they do not have to announce financial info publicly or deal with regulatory requirements for being a public company.
Do technology stocks increase a company’s value?
Not necessarily. Investing in stocks is always risky because they are market-based rather than intrinsic. This means that the company’s worth isn’t based on an expectation of its future earnings, but you can guess whether or not someone else will want to buy it.
What gross margin do you need to float on the stock market?
The amount of capital a firm needs to have will vary depending on the risk associated with the assets that are being financed, as well as management’s expectations for investment results. In general, firms need enough capital or assets to withstand unexpected risks and still meet obligations.


