A startup is hard work, and it takes a lot of energy and dedication to get the company off the ground. One of the most important things you need to do when starting a business is to allocate ownership shares.
Determining how a startup can give equity can be complicated, but it’s essential to get it right from the beginning so everyone involved is clear on their role and responsibilities.
Startups typically give equity in exchange for cash, services, or product. In some cases, a startup might give away equity for free in exchange for a commitment from the recipient to help promote the company or refer potential customers.
When it comes to negotiating an equity agreement, there are typically three primary considerations: how much equity should be granted, what rights should be attached to that equity, and when should those rights vest (that is, when do the recipients of the equity have the right to own it).
The amount of equity granted usually depends on how much money the startup has raised, how much value the startup has created (or is expected to make), and how vital the person receiving the equity is to the company.
Three important facts to keep in mind before giving away startup equity:
- When you give away equity in your startup, you’re giving away a piece of your company. This means that you’re giving away a part of the ownership and control of your company.
- You should only give away equity in your startup if you need to and if it’s the best option for your business. Otherwise, you’re better off keeping 100% ownership and control of your company.
- If you decide to give away equity in your startup, make sure that you get something in return, such as money, advice, or services. Otherwise, you’re just going to be giving away value for free.
One of the most common ways to give away equity is offering shares for free. Investors often see this as an excellent way to get more customers on board since they’ll have something tangible in return for their investment (shares).
Another popular method is convertible debt. This type of loan can be converted into equity at a later date, which means that if the startup reaches certain milestones or makes enough money, then part or all of it could be turned into stock options.
Converting debt into options provides startups with two things:
- An easy way to raise capital from investors who might not want to commit funds right away.
- An incentive for early employees and founders who receive monthly payments but don’t own any stock.
Startups also give away equity as it’s a great way to build trust with employees. Employees feel like they’re part of the company and that their contributions are appreciated, which increases morale and productivity.
In addition, startups that offer stock options as compensation for new employees are more innovative than those without such programs.
The research found that companies with generous stock-option plans tended to produce better products in later years – even after accounting for financial performance at the time.
If you want to invest in a startup, an equity investment is always the best route. This will give your company more control over its future and allow them to grow at its own pace. Equity investments can be made with or without dilution.
Let us look at six types of startup equity investments with and without dilution:
- Convertible debt – The investor agrees to convert all or part of their investment into equity at a predetermined price, usually after the startup has reached a certain level of revenue or other criteria being met.
- Preferred stock – The investor is given a share in the company but does not own any equity until the company pays them what is known as “pre-emptive rights.” This payment can be made in cash or through shares issued to them before collecting on their investment.
- Warrants – An agreement between two parties where one party issues warrants (a right but not an obligation) for something under specific circumstances, such as reaching a particular sales target within a specified period.
- SAFE – A Simple Agreement for Future Equity is a type of convertible debt instrument that is popular among startup investors. It’s simple to understand and doesn’t require any legal documents.
- Equity – When you issue equity, you’re selling a percentage of your company to someone else in exchange for money. This dilutes the founders’ ownership and changes the dynamics of the company’s ownership structure.
- Debt financing – Borrow money from banks or other lenders at fixed rates to buy equipment upfront and pay it off later.
The equity of a company is the total value that it has. This can be calculated by multiplying current assets with their present market values and dividing this number by the total liabilities plus preferred stock.
Startups are often started on less than $5 million in funding, which means they have to give away most or all of their equity to investors who believe in them.
Equity may not seem like much initially if you’re looking at your business as just one phase of your life’s work, but there are many different opportunities for entrepreneurs to grow their wealth over time – so don’t let anyone take what could continue to be yours.
How Much Equity Does A Startup Give?
A startup can be an exciting and rewarding experience, but it’s important to know what you’re getting into before starting this journey. One of the most important decisions you’ll make is how much equity to give away to your partners, employees, and investors.
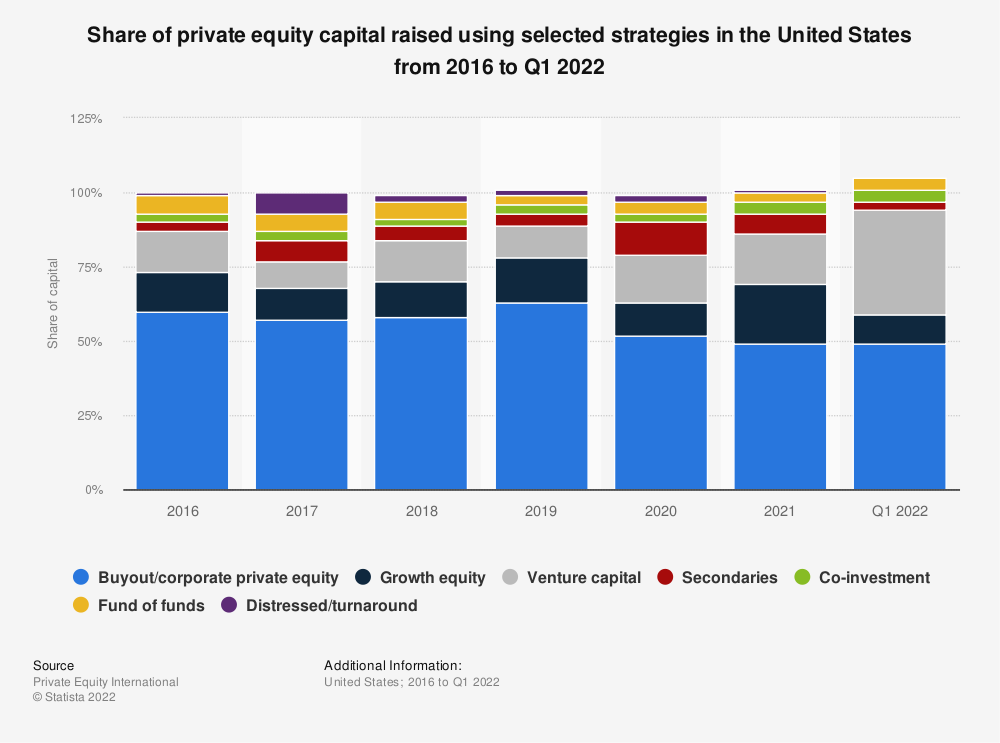
It depends on the startup. The amount of equity a startup gives ranges from nothing to 60% depending on what type of company it is and how much money they want to raise.
The more equity you have, the less likely you are to be able to sell your shares for cash because other people would need an ownership stake for them to receive payment or repayment from the sale of shares.
Startups often give away equity to attract talent and fuel growth. Let us look at three reasons why startups give away equity:
- Equity is a way to attract and retain talent. When someone joins a startup, they are taking on many risks and may not be compensated as well as they would be at a larger company. Offering equity can be a way to sweeten the deal and convince them to take the risk.
- Equity is a way to motivate people. When everyone in a company owns equity, it gives everyone a financial incentive to work hard and help the company grow. This can be especially important in early-stage startups where there may not be much money available for bonuses or other forms of compensation.
- It’s a way to raise money. Equity can be used as currency to attract new investors or partners into a company.
In general, founders want to ensure that they are equally invested in their success or failure. So they’ll often negotiate an equal share of ownership with each other instead of giving one person all of it.
This way, if one person decides to leave before retirement age (say, due to burnout), there will be someone else available who can step into that role and keep things going smoothly until they are ready to return full-time.
How Much Equity do Startup Founders Have?
One of the critical things you need to know is how much equity you have in your startup. This number can vary based on the stage of your company, how much money you’ve raised, and other factors.
It varies from startup to startup, but typically startup founders have a 20-30% equity stake in the company in exchange for starting the business.
In some cases, the founder may put up some money to get the business off the ground and receive a more significant percentage of equity as repayment. In other cases, the founder may not have any money invested in the company but will receive a smaller percentage of equity for their hard work.
Startup founders must have more equity in their company to feel confident that the hard work will be rewarded. Having a significant equity stake also encourages risk-taking and innovation, which drives successful companies.
Let us look at three reasons why startup founders should keep more equity:
- Founders are the ones who make the most significant risks and put in the most time and effort. They deserve to be rewarded for their hard work.
- Equity incentivizes founders to work harder and longer because they know that they will reap the benefits if their startup is successful.
- Giving founders more equity gives them a stronger incentive to stay on board and help grow their company. This can be crucial in the early stages when things are often challenging, and much work needs to be done.
Keeping more equity is essential for startup founders because it can provide them with financial resources if their company isn’t as successful as they had hoped.
Additionally, keeping some equity allows founders to participate in future rounds of funding, which can help them stay involved in the company’s growth and success.
Founders need to work with their cofounders or team members to determine what percentage works best for them as individuals and the company they are building.
What this means is there isn’t complex data on how much equity an entrepreneur should take, but it varies based on individual circumstances such as experience level and industry expertise.
How Much Equity Should Founding Members Get?
Determining how much equity to give founding members is one of the most critical decisions an entrepreneur will make. Too little, and you may not have the best people on your team; too much, and you might not have any money left to run your business.
Generally speaking, founding members should get a more significant percentage of equity than later employees since they are taking on more risk and contributing more to the company at the outset.
A good rule of thumb is to split the equity equally among co-founders at the earliest stages of a company’s development and then adjust allocations as the company matures and its value grows.
It’s also important to remember that co-founders should be rewarded for their contributions not only in terms of cash or equity but also in terms of control and decision-making power within the company.
Do Startup Founders Have To Pay For Shares?
When you’re starting a new business, there are a lot of important decisions to make. One question that often comes up is whether the founders have to pay for their shares.
Startup founders do not have to pay for shares. The founder’s company ownership is typically 100% vested over time. There are no additional fees or charges associated with partial vesting of claims yet to be earned.
In addition, many startups will offer equity in the form of stock options as part of an overall compensation package for executives and employees alike.
The value of these stocks will fluctuate based on both share price and the number of options outstanding at any given time – meaning that you can make money even if your startup doesn’t reach its valuation goal.
It’s also possible to sell some or all one’s holdings before retirement eligibility if they so choose (although this generally isn’t recommended).
Conclusion
Startups are all about equity. How much you get, how to determine who gets it and what is fair depends on the company’s needs at different stages of development.
Startup founders should be sure they’re getting a good deal for themselves and their employees by considering these questions in this article before making any decisions around equity allocation.
Quick Answers To Frequently Asked Questions
Are startups required to have an incentive stock option or an early employee stock purchase plan?
When it comes to startup stock options and early employee stock purchase plans, there are a number of different factors that go into the decision. The most important consideration for startups is whether they have an incentive stock option or not. Either one can be beneficial in some ways but neither will necessarily lead to success by themselves. If your company does not offer either kind of plan, you may need to rethink how you compensate employees if growth is slow and revenue isn’t increasing.
Is there income tax on startup employee equity ownership?
There is no income tax on startup employee equity ownership, as long as the equity is earned through providing services to the startup. However, there may be other taxes (e.g., capital gains tax) that apply when the equity is sold or liquidated. Consult with a qualified tax advisor to ensure you are paying all the appropriate taxes on your startup equity ownership.
Difference between sweat equity compensation and founder equity dilution?
There is a big difference between sweat equity compensation and founder equity dilution. Sweat equity compensation is when an individual contributes services to a company in exchange for shares in the company. Founder equity dilution, on the other hand, is when the founders’ percentage of ownership in the company decreases due to the issuance of new shares to employees, consultants, or investors.
Difference between the common stock unit and the restricted stock unit?
The main difference between a common stock unit and a restricted stock unit is that the holder of a common stock unit is entitled to vote on company matters, while the holder of a restricted stock unit is not.
A common stock unit is essentially just like owning shares of common stock, while a restricted stock unit represents ownership in shares of company stock but with certain restrictions attached. For example, the company may reserve the right to buy back or retire the restricted shares at some point in the future.
Difference between section 83B and series A option pool?
Series A option pool is set up to incentivize early employees and investors. These stakeholders receive stock options in the company that can be exercised after a certain vesting period. The Series A option pool also allows the company to issue new shares later on to attract new investors and employees.
Section 83B is an IRS provision that allows taxpayers who receive restricted stock units (RSUs) from their employers to be taxed when they actually receive the RSUs, rather than when they vest. This can save employees a lot of money in taxes, but it’s important to understand the rules and limitations around Section 83B before taking advantage of it.
Where can I find the fair market value of authorized shares?
The fair market value of an authorized share is the price at which a willing buyer and seller would agree to exchange their shares.
The easiest way to find the fair market value of your company’s stock is by looking at how other companies in the same industry have been trading. You can use a search engine like Google Finance or Yahoo! Finance, or you can visit websites that track stocks for individual industries.
Are employee stock options in the liquidation preference?
Yes. Employee stock options are included in the liquidation preference because they represent a form of compensation that can be exercised at any time, unlike other forms of equity compensation such as restricted stock units (RSUs), which must be vested before they can be exercisable.
When an employee exercises an option to purchase shares of company stock, the market value of those shares is immediately raised and put into effect as payment for services rendered up until that point; this makes it more difficult for shareholders to redeem their holdings should business prospects take a downturn.
Difference between an equity grant and equity offer issued shares?
An equity grant is when a company awards stock options or restricted shares to an employee. An equity offering is when a company offers to sell shares of its stock to the public.
When a company makes an equity offering, it’s selling ownership of the company to the public. This means that anyone who buys shares will own a piece of the company and have a say in how it’s run. When a company makes an equity grant, it’s awarding stock options or restricted shares to employees. This means that employees will own stock in the company but won’t have any say in how it’s run until they exercise their options or sell their shares.
Do potential investors of vested shares receive voting rights in San Francisco?
In San Francisco, investors of vested shares typically receive voting rights. This means that the shareholders are able to vote on decisions that affect the company, such as who will become the company’s directors or whether they should pursue a certain course of action. Of course, there may be some exceptions depending on the company’s bylaws or if the investor is acting in a fiduciary role.
Difference between equity share and equity distribution?
An equity share is a type of security that represents an ownership interest in a corporation. Equity shares represent a residual claim on the assets of the company after all liabilities are paid.
An equity distribution is when a company distributes some or all of its equity to its shareholders. A distribution can be in the form of cash, property, or stock. When a company makes an equity distribution, it reduces the amount of equity that’s available for future distributions. This can have a negative impact on the value of the shares.
Difference between a convertible note and capital gain?
A capital gain is the profit made when you sell an asset for more than you paid for it. A convertible note, on the other hand, is a debt instrument in which the issuer promises to pay off a part of your investment with interest and/or return some number of shares at a pre-determined price upon conversion into common stock.
The key difference between these two events is that with a capital gain you make money by selling an asset but have to pay taxes on this sale before receiving any funds from buyers – whereas if someone pays cash for your convertible note they will be doing so without paying any taxes beforehand (which can really add up over time).
How can I get an angel investor to buy my outstanding shares?
The best way to get an angel investor is through a seed round.
An Angel Investment Network (AION) will often invest small amounts of capital from its members in early-stage companies that have the potential for growth but require additional investment.
Angel Investors are typically individuals who put their money into businesses or projects they believe in with the hope that they will be rewarded with either partial ownership or profit-sharing once the company becomes successful.
This type of investment can come in many forms including personal loans, equity shares, and/or property stakes. They may offer financial support by lending you money at below-market rates if they like what they see so far; this is called “pre-seed”.


